Foundation Models for Trajectory Planning in Autonomous Driving: A Review of Progress and Open Challenges
Abstract
arXiv 2025 | Comprehensive review of 37 foundation-model-based approaches for trajectory planning in autonomous driving assessing openness and their inclusion in a novel taxonomy.
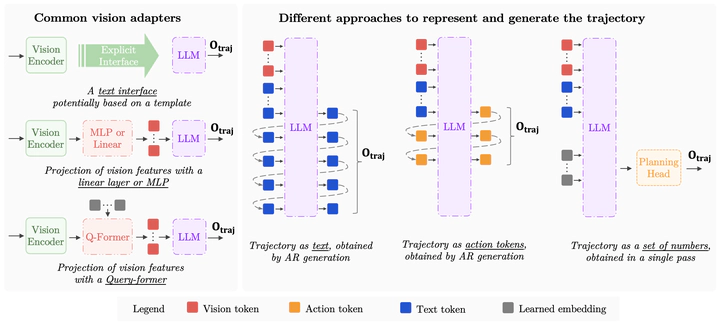
The emergence of multi-modal foundation models has markedly transformed autonomous driving, shifting away from conventional and largely hand-crafted design choices towards unified, foundation-model-based approaches capable of directly inferring motion trajectories from raw sensory inputs. This new class of methods can also incorporate natural language as an additional modality, with Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models serving as a representative example. In this review, we provide a comprehensive examination of such methods through a unifying taxonomy to critically evaluate their architectural design choices, methodological strengths, and inherent capabilities and limitations. Our survey covers 37 recently proposed approaches spanning the landscape of trajectory planning with foundation models. Furthermore, we assess these approaches with respect to the openness of their source code and datasets, providing valuable information to practitioners and researchers. We also provide an accompanying webpage that catalogues the methods based on our taxonomy, available at: github.com/fiveai/FMs-for-driving-trajectories →.